Artificial intelligence – once something out of a science fiction movie, smart and self-learning systems are now everywhere. They control vehicles, tell us if our bus is going to be late, manage investment funds, and make unerring medical diagnoses.
The performance of artificial intelligence has improved massively in recent years and has catalyzed a major transformation. Similar to the way machines took over the burden of monotonous physical tasks at the beginning of the 20th century, AI now has the potential to automate monotonous intellectual tasks. It doesn’t replace humans; it can relieve them.Artificial intelligence is primarily used to assist in tasks where similar decisions have to be made repeatedly. The legal sector is a good example of this, as shown by the emerging market of legal AI providers.
Have you ever wondered what legal AI technologies are all about? This blog article explains what goes on behind the scenes without requiring you to have a computer science degree – that’s a promise!
Definition of AI (Artificial Intelligence)
Artificial intelligence is a very general term for which various definitions exist; but simply put, an AI is a machine that possesses human-like intelligence.
However, this intelligence is currently limited to solving concrete problems. It’s based on algorithms that make decisions via a learning process within a narrowly defined framework.
This clearly distinguishes the AI used today from AI that is self-aware and possesses emotional or social intelligence, which has, so far, been reserved only for our imagination. In reality, this kind of omnipotent AI is still a thing of the future.
Artificial intelligence (AI) refers to technical programs that use human-like intelligence to learn ways to solve specific problems.
Machine Learning – Key AI Technology
What is Machine Learning?
Machine learning is a common method by which an algorithm gains intelligence.
A classical computer program, without AI, uses data and rules specifically defined by programmers to calculate a result. With machine learning, the tables are turned: the artificial intelligence receives data and results and figures out the rules on its own.
The process in which millions of parameters within a model are adjusted is called AI training. The algorithm can subsequently apply the rules it defines independently to provide answers to questions of the same kind.
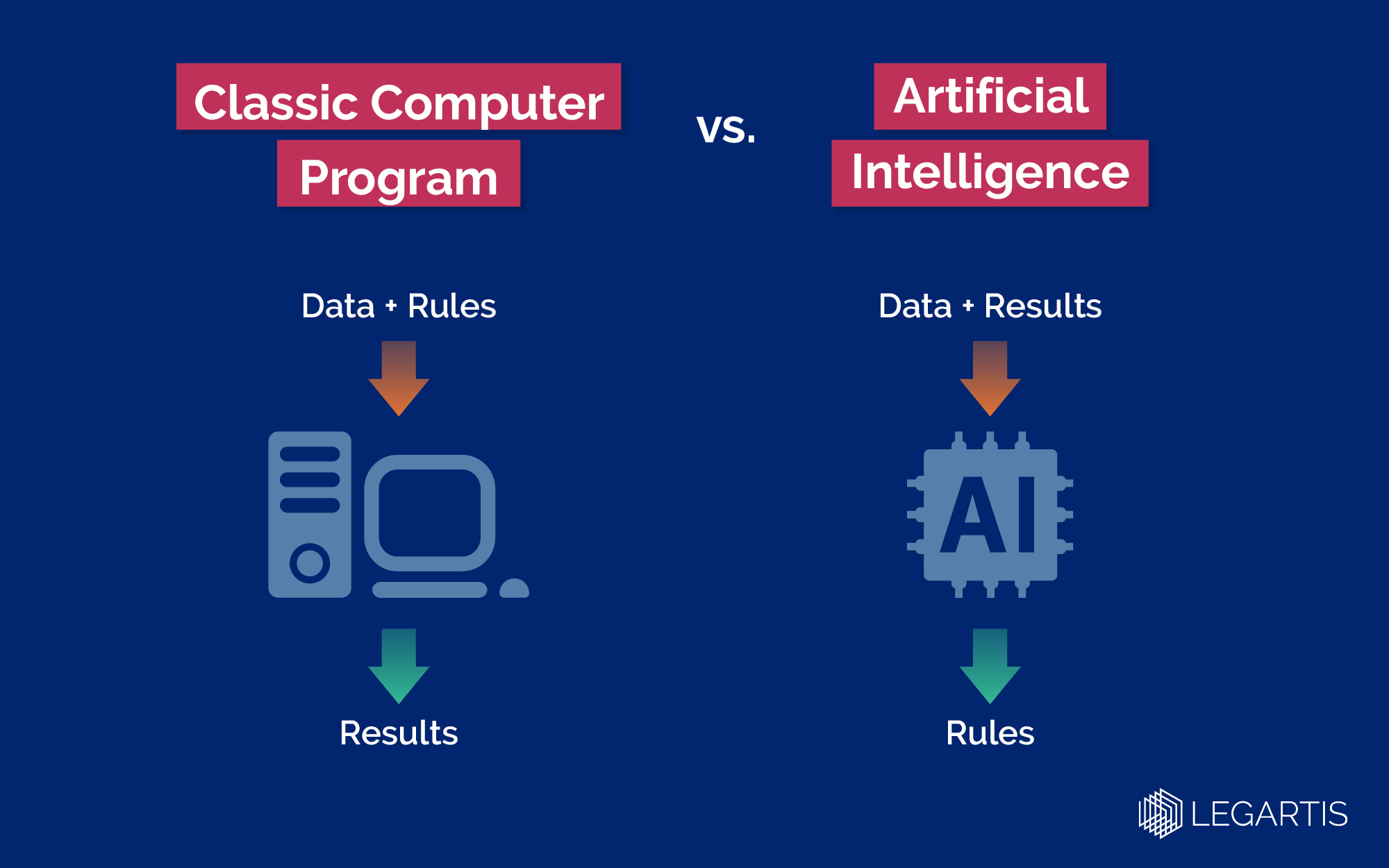
Let's take a simple example to understand the benefits of artificial intelligence. Imagine you want to run a program that can distinguish between cats and dogs.
- With a classic computer program, you would now have to feed it rules. What makes a cat a cat and a dog a dog? Is it the shape of the ears or the position of the tail? Hard to say, isn't it? And it is even harder to express as a concrete rule.
- With artificial intelligence, this problem doesn’t arise. It’s relatively easy to provide the necessary data and results for its training; you feed it pictures of dogs and cats and tell it whether it’s a dog or a cat. After this training, the AI will have learned its own rules to tell the animals apart.
Supervised vs. Unsupervised Learning
Machine learning is the process of taking data and results (examples of correct solutions) and generating rules that can then be applied to new data. A distinction is made between two types of machine learning:
- Supervised learning
- Unsupervised learning
In supervised learning, functions whose target metric is known are determined. During training, humans manually correct any incorrect results of the AI and in this way help it to improve. This is also how Legartis' AI is trained.
In unsupervised learning, the AI extracts the target variable from the data itself. The human doesn't have to define or control a target.

AI in the Legal Environment
Artificial intelligence is becoming more and more prevalent in the legal environment – and no wonder, because it’s made for it! But why?
Lawyers are often searching for a needle in a haystack in their work, sifting through thousands of pages of written material: legal texts, company documents, archived correspondence, old contracts and rulings …
They devote themselves to questions such as:
- I have 8,000 contracts. Which of them need to be adapted because of Brexit?
- Which of my contracts already contain the new disclaimer?
- Which of our 4,000 contracts are active and which are inactive?
What constitutes a ton of manual work for us humans is child's play for an AI, under certain conditions, because all of these texts are nothing more than data and results from which it can derive rules. Legal tech AI applications take much of the burden off legal departments in narrowly defined target areas such as these.
Legartis' Legal AI is specially trained for automated contract review in the pre-signing phase. The solution:
- analyses the full contract content in seconds,
- compares it with company standards,
- categorizes content into non-permissible clauses and clauses to be verified,
- highlights missing clauses in contracts, and
- identifies risks in contracts.
In this way, lawyers can be intelligently guided through the contract review process, saving time and enabling them to focus on value-added tasks.
Artificial Intelligence: 3 Key Takeaways
The legal tech market offers countless solutions for the phases of the contract life cycle. But not everything with “Legal Tech” in the name uses AI technology!
- AI (artificial intelligence) is the ability of an intelligent computer program to mimic human skills such as logical reasoning, learning, planning, and creativity. However, these skills are not universal; rather, they always remain confined to a narrowly defined area.
- Machine learning is a method of training AI. It uses data and results from which the AI independently derives rules. It can then apply these rules to new data.
- The use of artificial intelligence is particularly suitable for the legal sector. Trained legal tech AI algorithms can examine text-heavy contracts in a matter of seconds and even enable laypersons to review contracts.
Legal AI Glossary
These are the terms you should be familiar with surrounding artificial intelligence in legal tech
AI: something man-made that perceives and can act intelligently based on its findings.
Machine learning: algorithms that are able to learn from their mistakes.
NLP: a method that enables computers to understand spoken or written language.
Legal tech: digital applications and systems that help deliver legal services more efficiently and make them accessible to a greater number of people.
Contract lifecycle: the process of contract management, from drafting to signing.
Contract review in the pre-signing phase: review of the draft contract in the pre-contractual phase, before the contract is signed.
Recommended Articles
Trends 2025: AI in Contract Analysis
The latest trends in Large Language Models (LLMs) show a shift towards greater efficiency, advanced AI agents and wider adoption across all industries. AI models are becoming..
KPIs in Contract Review
KPIs (Key Performance Indicators) are indicators that are used to measure performance and determine whether specified targets are being achieved. This applies to companies,..
Legal AI Talk: Latest Large Language Model Trends
AI and Large Language Models (LLMs) are revolutionizing the legal industry, streamlining contract analysis, document automation, and research with greater precision...




